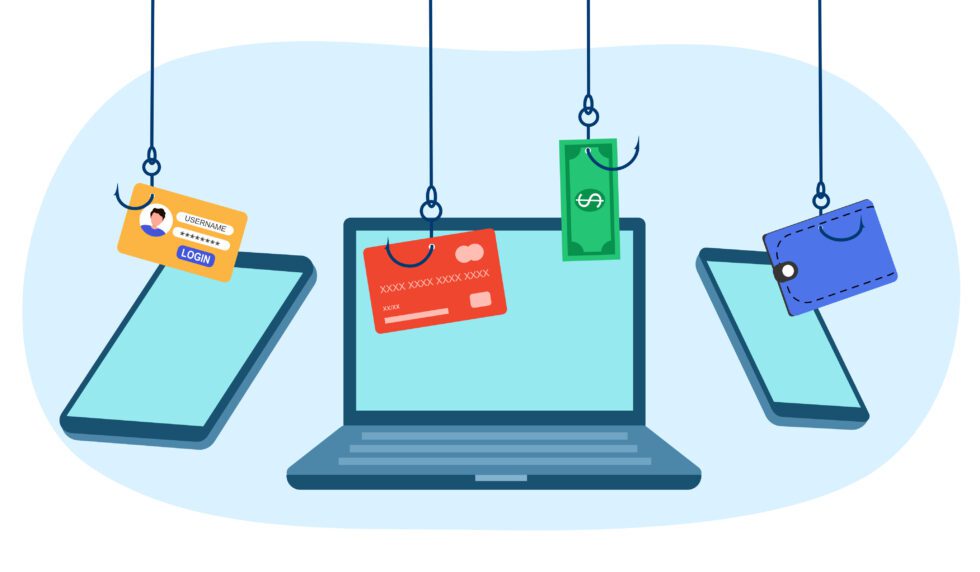
Scammers may contact you by email, text, or phone, posing as legitimate businesses. They often imitate businesses you trust and use regularly, such as your bank, internet or telecommunications provider. This scam is sometimes called “phishing”. Whichever approach is used, the scammer’s goal is the same – to obtain your personal information and commit fraud against you.
Phishing emails often use the same branding, logos, and format of communication as one of your trusted providers. A phishing email might state there is a problem with your bank account, such as a security breach, and ask you to click on a link to provide your personal details, which can later be used to commit identity fraud, or steal money from your bank account. A common approach used by text scammers is sending out customer surveys that offer a prize for participating, in order to obtain your personal information to commit fraud at a later date.
Being online is part of our daily lives as we work, bank, shop and stay connected with friends and family. Connectivity is making our lives easier, but there are risks. Protecting yourself online is simple, so don’t wait until you become the victim of cyber crime.


Be wary of ‘out of the blue’ contact
A telecommunications company would never call a customer out of the blue and request remote access to their device/s. If this happens to you, it is a scam, and the best action you can take is to hang up.
It is only when a customer has requested assistance to troubleshoot a technical issue, that a provider will suggest remote access. So the request will always be initiated by the customer and additional security measures will be in place.
Similarly, a telco would never ask for credit card details over the phone to fix or diagnose a problem.
Stop and think. Is this for real?
If you receive a suspicious call, email or text: Stop and think. Is this for real?
Never click on the links or attachments in emails and text messages that ask you to login or verify your password. They could easily be phishing messages sent by scammers. Instead, go to the legitimate website and log in from there.
A telecommunications company would never call a customer out of the blue and request remote access to their device/s. If this happens to you, it is a scam, and the best action you can take is to hang up.
Think about what the scammer is trying to achieve
Scammers may all work in different ways, but generally speaking the end goals are to:
- Get access to your finances.
- Steal your identity.
- Buy goods and services.
- Access your business networks or systems.
Source CERTNZ
What to do if you think you have received a scam call
1. If you receive an unexpected phone call that seems suspicious, the best action to take is to hang up. Do not share any personal information with the caller.
2. If the caller has told you they are from a particular company, ring the company (find their number elsewhere, don’t call back the number they called you from) and alert them to the call you have just received. They will let you know if it was a legitimate call.
Top Tips for staying safe online:
Improve your security with these tips:
Password protect all your devices. Use strong alpha-numeric passwords and include upper and lower case letters. It’s a good idea to use a password manager to create unique passphrases.
- Change your passwords regularly and use different passwords for each online account
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible (see below for further detail).
- Set up a PIN for your voice mail.
- Secure your computer and devices with firewalls, anti-virus software and up to date operating software.
- Only use secure WiFi connections.
- Protect your WiFi with a strong password and encryption settings.
- Keep your devices and apps up to date.
- Be aware of scams and don’t click on unexpected attachments or links you don’t recognise.
- Limit the amount of identity information you post online.
- Check your privacy settings for social media accounts.
- Regularly back up your data.
About 2FA and MFA
2FA or MFA (2 factor or multi-factor authentication) is when along with having to enter your password to access a secure website, you are also required to take a second step to confirm your identity.
Often this second step involves sending a code via SMS text message to your mobile phone for you to enter into the website. Many websites are now offering alternative means for this second step authentication, such as getting you to install a special authentication app on your phone. Where possible, try to use the app method and avoid relying on an SMS text message or a phone call for this second step authentication.
More information
For more tips on protecting yourself online, check out the website of your telecommunications provider or visit: